
239Alferov Scientific Mission
How the CubeSat Helps Explore Cosmic Events
On December 28, 2025, four 16U Space-π smallsats were launched as part of the Roscosmos Soyuz-2.1b/ Aist-2T launch.
On December 28, 2025 4 16U Space-π smallsats were launched as part of the Roscosmos Soyuz-2.1b/ Aist-2T launch.
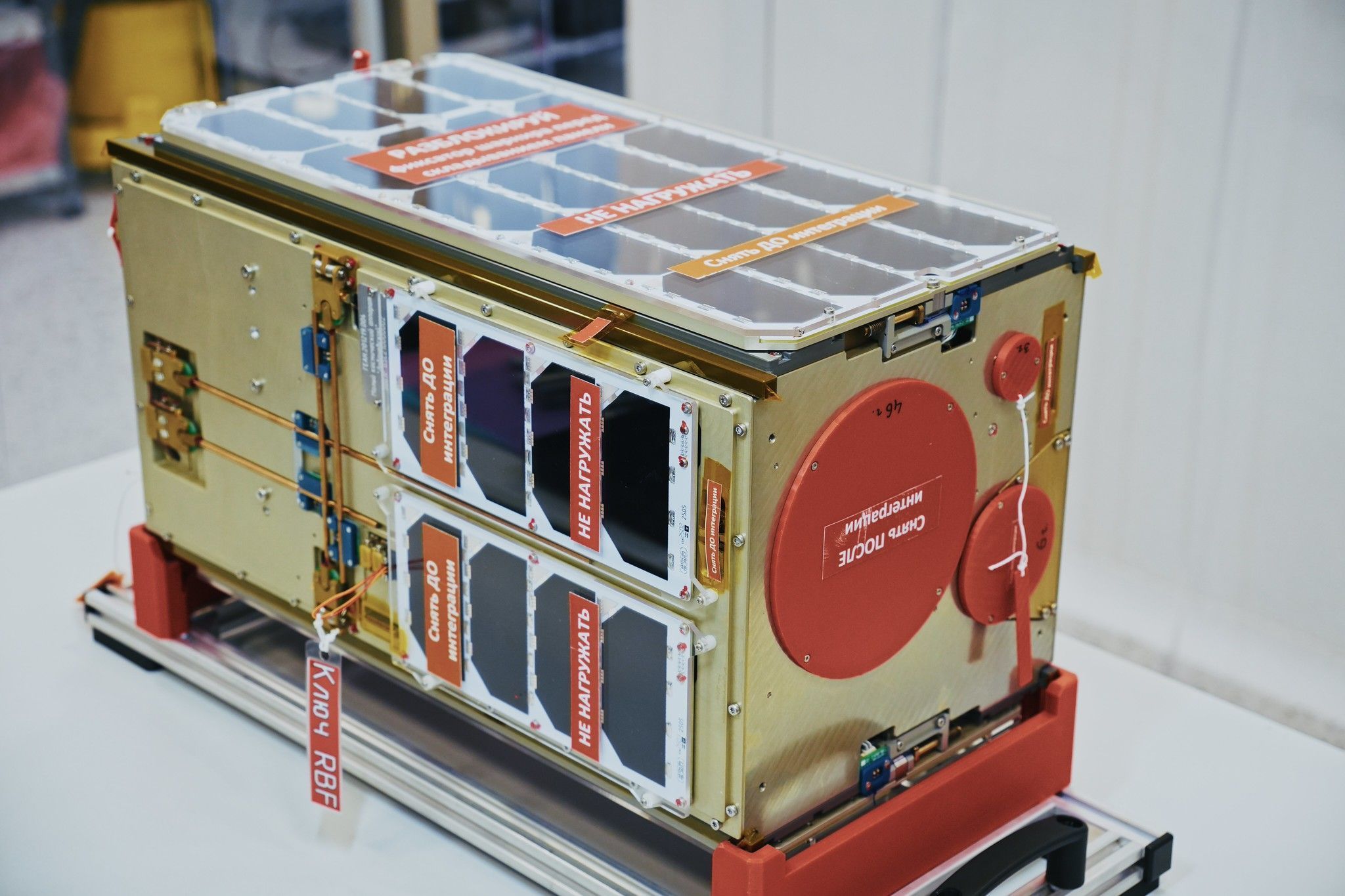

The 16U «Lobachevsky» CubeSat, created by the Nizhny Novgorod State University named after N. I. Lobachevsky, based on the 16U satellite platform of Geoscan LLC, is equipped with multispectral and hyperspectral cameras for agroecology tasks, as well as an amateur FM radio repeater with an integrated hardware and software package for testing memristive devices in space. The first signals from the cubesat were received by the SONIX station in Omsk.
During the space experiment, it is planned to obtain satellite spectral images of reference areas of forests and agricultural crops, i.e. areas with known agrophysical characteristics, or subsequent confirmation on the ground of the conditions of the captured areas. Students will conduct a comparative analysis of the received ground and space data. The obtained results will become an experimental base for educational research on the following topics:
stress foci identification in forest near populated areas of the Nizhny Novgorod region, as well as identification of plant stress factors
The spread of invasive woody and perennial herbaceous plants in the Nizhny Novgorod region, such as ash maple, Japanese rhinutria, Canadian goldenrod and others that aggressively displace native vegetation species
search and analysis of the activity of smoldering peat bogs in the Nizhny Novgorod region.
For full-fledged experimental work, students learn about the principles of spectral photography, its physical nature, and the possibilities of using spectral data to remotely determine plant and soil conditions.
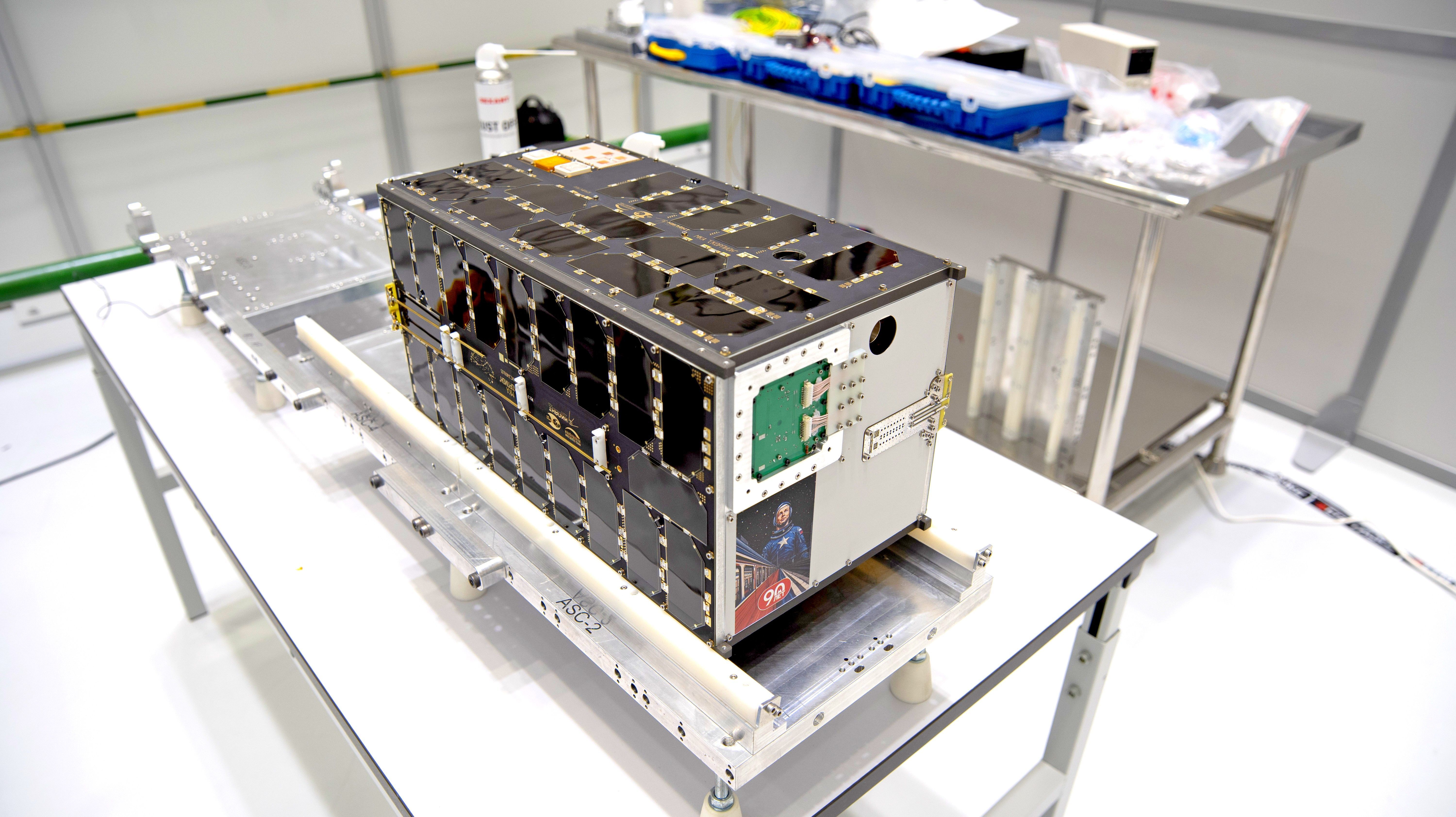
The 16U «Scorpio» CubeSat, developed by the D. V. Skobeltsyn Scientific Research Institute of Nuclear Physics (Moscow State University) based on the NILACT-DOSAAF 16U satellite platform, contains equipment for space experiments on space weather, microbiology, registration of extragalactic gamma-ray bursts and transients, monitoring of radiation and fluxes of charged particles in low Earth orbit.
«Scorpio» is designed to study the effects of space on living organisms, as well as to develop ways to search for microorganisms on space objects and observe rapid changes in radiation in Earth's orbit.
There are six devices installed on the cubesat:
1. Track gamma-ray spectrometer. It is designed to study gamma-ray bursts of various types. It consists of four identical modules with a scintillator and sensitive elements — silicon photomultipliers.
2. SONNET (a system of optical observations of energetic transients). It is intended for the study of energetic transient phenomena in the Earth's atmosphere.
3. BIOL (biological orbital laboratory). It is designed to study the dynamics of the physiological state of chlorella by fluorescent glow in space flight conditions.
4. BIOL-2. It is designed to study the effect of space flight conditions and cerium preparations on the vital activity of microorganisms in eight airtight containers by measuring their fluorescence levels.
5. KODIZ-2 (combined radiation detector). It is designed to register the fluxes of electrons, protons and nuclei of cosmic radiation in three mutually perpendicular directions.
6. ECG (charged particle energy analyzer). It is designed to monitor plasma flows in near-Earth orbits.
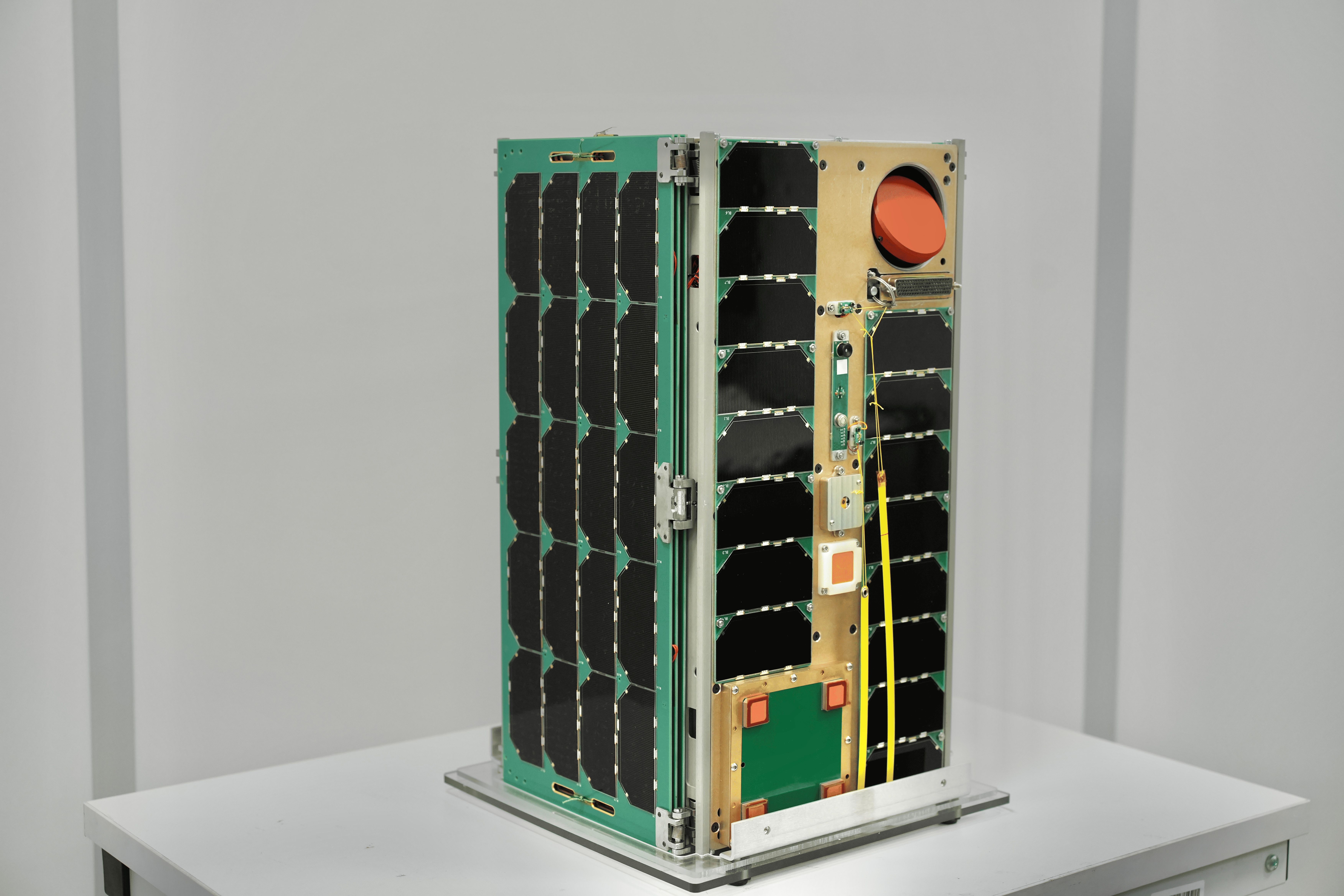

The «Polytech Universe-6» satellite (hereinafter referred to as PU-6), a 16U CubeSat from St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, developed on the basis of the 16U satellite platform of STC LLC, to measure the level of electromagnetic radiation in various frequency ranges to create a model for the distribution of these levels and analyze the level of "electromagnetic pollution".
Basic experiments:
1. Construction of territorial maps of the distribution of electromagnetic radiation levels from the Earth's surface. Analysis and comparison of the EMR data obtained with PU-3 and PU-6 (Polytech Universe-3 is a previously launched satellite of the university within the framework of the project). Refinement of intense radiation points using two metrics from both satellites.
2. Analysis of the data transmitted in the AIS system from PU-6, addition of the existing database (collected from PU-5), optimization and modernization of the existing service visualization of results. Speeding up the service.
3. Design and development of a satellite data receiving station, analysis of telemetry received from the PU-6 satellite, etc. Creation of a satellite telemetry visualization service, tracking and analytics of changing QMS metrics.
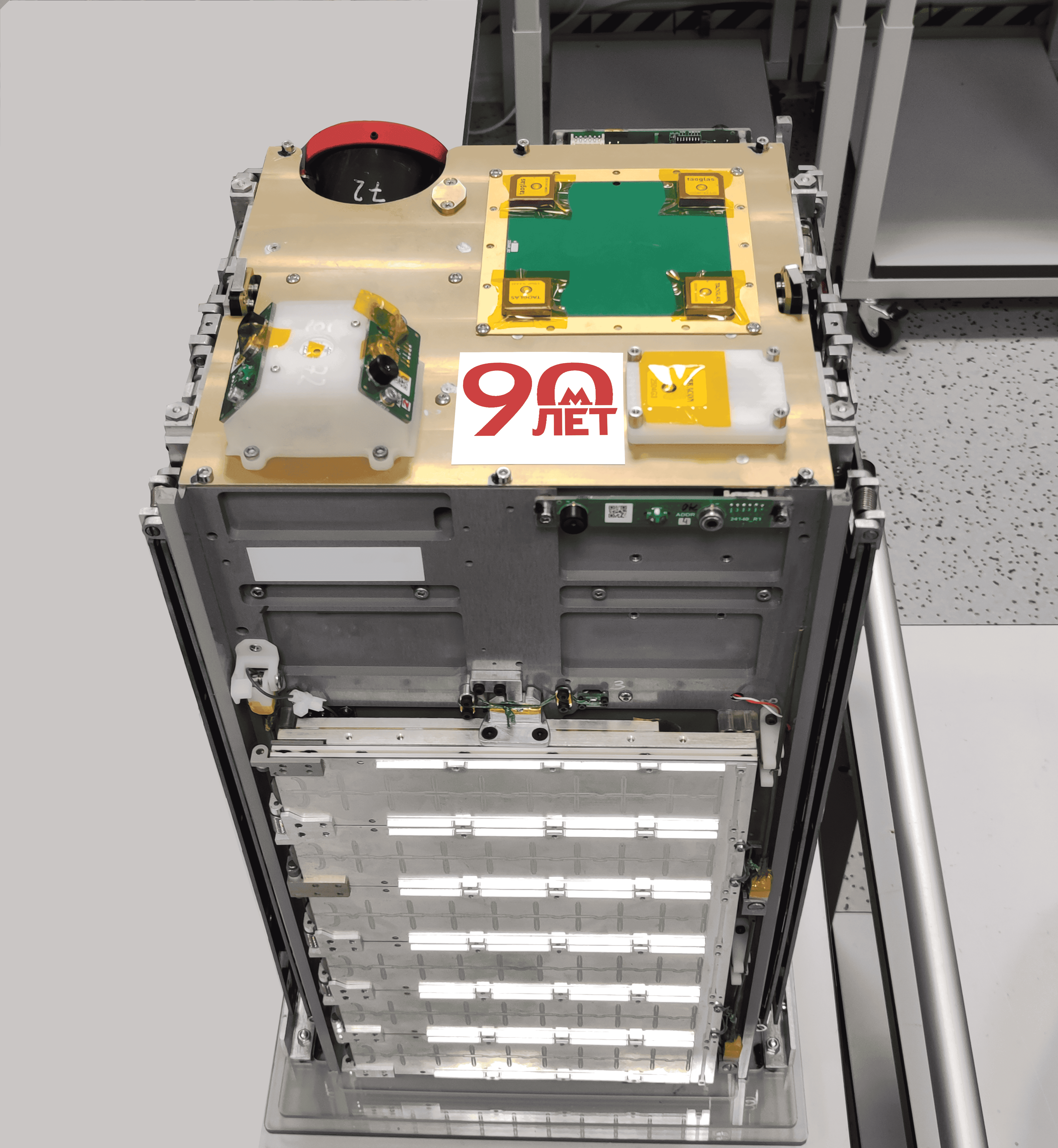
The «Aist-ST» 16U CubeSat was created by the Samara National Research University named after Academician S.P. Korolev on the basis of the 16U satellite platform of STC LLC in order to experimentally test radar equipment on a small spacecraft, as well as to study the rate of contamination of satellite elements by products of its own external atmosphere. The students planned to perform the following experiments:
1. Environmental monitoring of changes in snow cover height on Mount Elbrus;
2. Monitoring of ice melting in the waters of the Northern Sea Route to ensure the safety of navigation;
3. Assessment of the impact of spacecraft materials on surface contamination in the first months of flight.
All of the above vehicles were launched in launch containers developed by the private space company Aerospace Capital. The operator of the Soyuz-2.1b/Aist-2T launch vehicle mission is Roscosmos State Corporation, Glavkosmos JSC (part of Roscosmos State Corporation) acting as the head integrator of the associated payload launch and provides the launch service.
As part of the celebration of the 90th anniversary of the Moscow metro, spacecraft with a themed image of «Metrosha» and an anniversary logo went into Earth orbit. A child's drawing was applied to one of the satellites.

We will write to you only when something interesting appears,
no space junk